Gum infection, also known as periodontal disease, is a bacterial infection that affects the gums, ligaments, and bones that support the teeth. It is a common condition that can range from mild gingivitis to severe periodontitis, and if left untreated, it can lead to tooth loss. In this article, we will discuss gum infection in detail, including its symptoms, causes, gum infection stages (types), other types of gum disease, treatment, home remedies, complications, and prevention.
Gum infection is caused by the buildup of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on teeth and gums. Plaque can harden into tartar, which can only be removed by a dental professional. The bacteria in plaque and tartar produce toxins that can damage the gums and other tissues that support the teeth. Over time, this can lead to inflammation, infection, and the loss of bone and tissue that support the teeth.
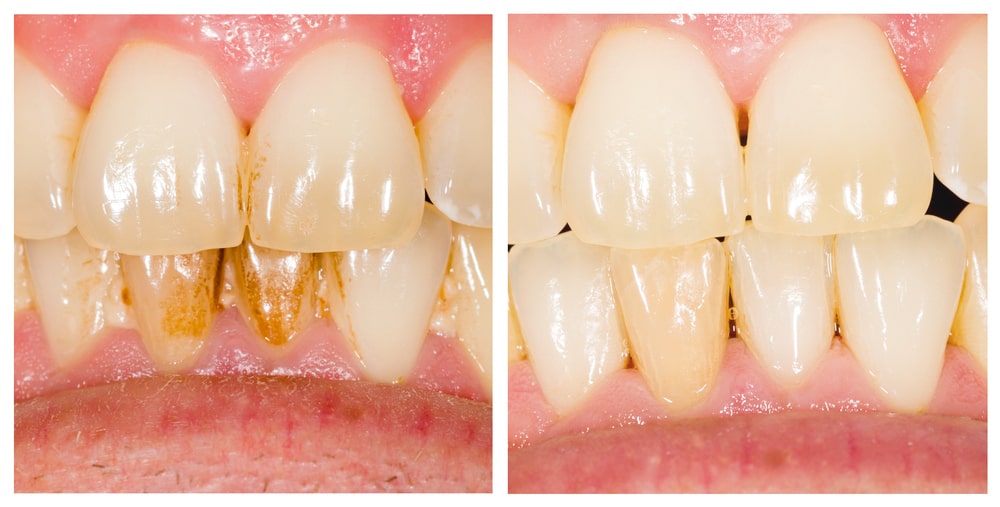
Gum infection is a common condition that affects people of all ages. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), nearly half of adults in the United States have some form of gum disease. Gum infection is more common in older adults, smokers, and people with diabetes or weakened immune systems.
Gum Infection Symptoms
Gum infection, also known as periodontal disease, can have various symptoms, including:
- Red, swollen, or tender gums: Infected gums often appear red, swollen, and feel tender to the touch.
- Bleeding gums: One of the earliest signs of gum infection is bleeding gums while brushing or flossing.
- Bad breath: Chronic bad breath, also known as halitosis, is a common symptom of gum infection.
- Receding gums: Gum infection can cause the gums to pull away from the teeth, exposing the roots.
- Tooth sensitivity: As the gums recede, the tooth roots become exposed and can be sensitive to hot or cold temperatures.
- Loose teeth: As gum infection progresses, the teeth can become loose and even fall out.
- Pain when chewing: Gum infection can cause pain when chewing or biting down on food.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to schedule a consultation in our dental clinic in Jerusalem as soon as possible to prevent further damage to your gums and teeth.
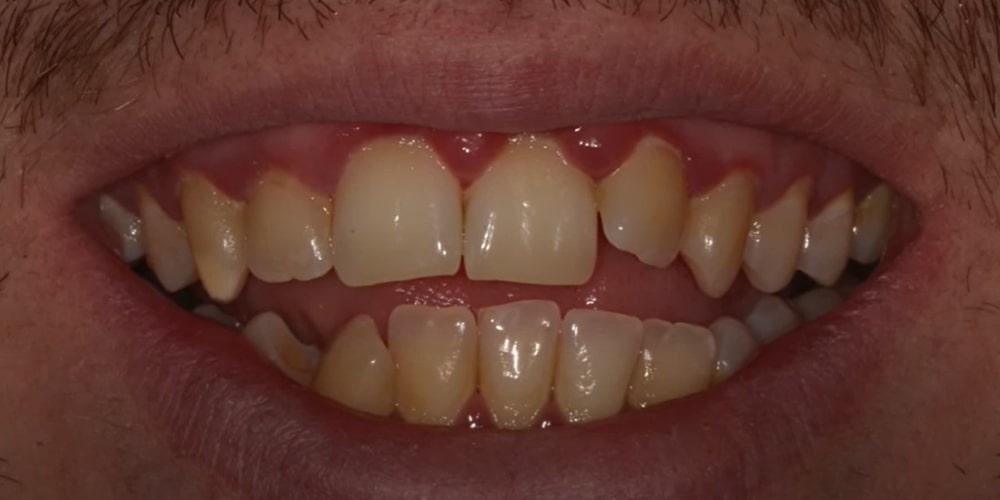
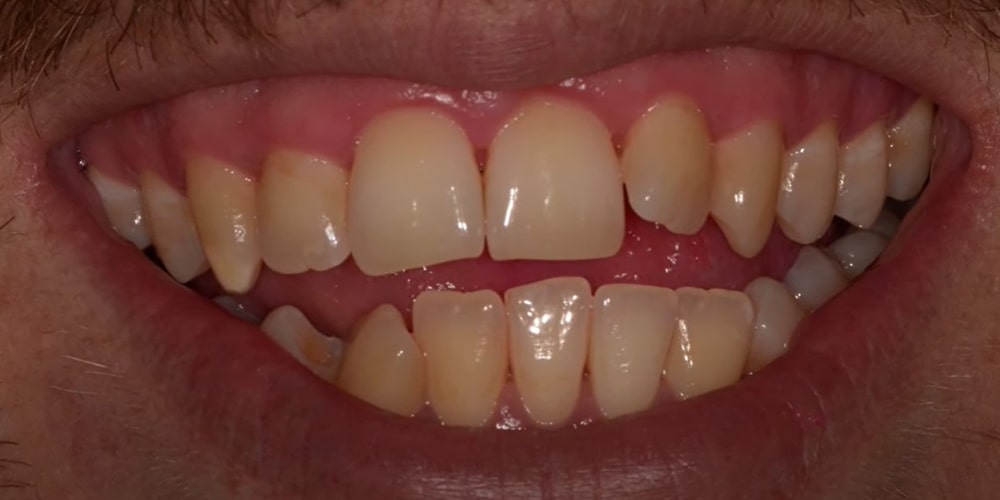
Causes
Gum infection is caused by a buildup of plaque and bacteria on the teeth and gums. Some common causes of gum infection include:
- Poor oral hygiene: Not brushing and flossing regularly can allow plaque to build up on the teeth and gums, leading to gum infection. Click here to learn how to brush your teeth properly.
- Smoking: Smoking weakens the immune system and can make it harder for the body to fight off gum infections.
- Genetics: Some people may be more prone to gum infection due to genetic factors.
- Medications: Certain medications can cause dry mouth, which can lead to a buildup of bacteria in the mouth and an increased risk of gum infection.
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal changes during pregnancy, puberty, and menopause can make the gums more sensitive and increase the risk of gum infection.
- Health conditions: Certain health conditions, such as diabetes and HIV, can make it harder for the body to fight off gum infections.
- Poor nutrition: A diet high in sugar and processed foods can contribute to gum infection by providing a food source for bacteria in the mouth.
It is important to maintain good oral hygiene habits and visit a dentist regularly to prevent gum infections from developing.
Gum Infection Stages (Types)
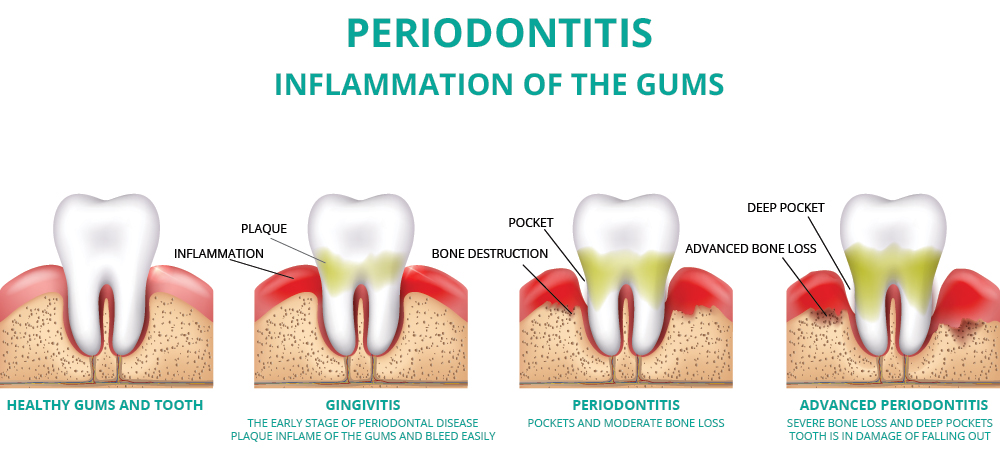
There are two main types of gum infection, known as gingivitis and periodontitis.
- Gingivitis: Gingivitis is the milder form of gum infection and occurs when the gums become inflamed due to a buildup of plaque and bacteria. Gingivitis is reversible with proper dental hygiene and professional cleaning.
- Periodontitis: Periodontitis is a more severe form of gum infection that occurs when the gum infection is left untreated and progresses to the underlying bone and tissues that support the teeth. Periodontitis causes the gums to pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that become infected with bacteria. Treatment for periodontitis may include scaling and root planing, antibiotics, or even surgery, depending on the severity of the infection.
Both types of gum infection can be prevented with good oral hygiene, such as brushing twice daily, flossing daily, and regular dental checkups and cleanings. If you experience any symptoms of gum infection, it is important to contact us for diagnosis and treatment.
Other Types Of Gum Disease
Gum disease can take on several different types. These include:
- Aggressive periodontitis: Aggressive periodontitis is a rare but severe form of gum disease that can lead to rapid destruction of the gums and bone tissue. This type of gum disease is most commonly found in young adults and is often associated with a genetic predisposition.
- Periodontitis caused by systemic diseases: Certain diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and HIV can contribute to the development and progression of gum disease.
- Necrotizing periodontal disease: This type of gum disease is a rare and severe form of periodontitis that causes the death of gum tissue, ligaments, and bone. Symptoms include painful and bleeding gums, bad breath, and ulcers.
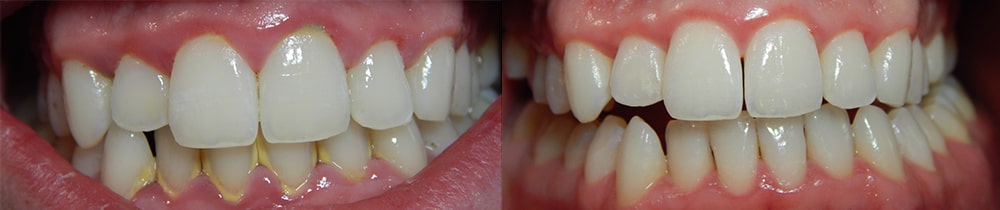
Treatment
The treatment for a gum infection, or periodontal disease, can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Mild cases can often be treated with improved oral hygiene practices, such as brushing and flossing regularly, and using an antiseptic mouthwash. The use of antiseptic mouthwash requires a prescription from the dentist for limited use of up to about a week and only after tartar cleaning.
For more severe cases, treatment may include:
- Scaling and root planing: This involves deep cleaning of the teeth and gums to remove plaque and tartar buildup from above and below the gum line.
- Antibiotics: Oral or topical antibiotics may be prescribed to help control the infection.
- Gum surgery: In advanced cases of periodontal disease, surgical treatment may be necessary to remove damaged gum tissue and reposition healthy gum tissue.
- Bone grafting: If the infection has caused bone loss, bone grafting may be necessary to help regenerate bone tissue.
- Laser therapy: In some cases, a dental laser may be used to remove infected tissue and promote healing.
Home Remedies
While it’s important to seek professional treatment for gum infections, there are some home remedies that may help alleviate symptoms and support oral health. These remedies include:
- Saltwater rinse: A saltwater rinse can help reduce inflammation and kill bacteria in the mouth. Dissolve a teaspoon of salt in warm water and swish the solution around the mouth for 30 seconds before spitting it out.
- Tea tree oil: Diluted tea tree oil can be applied to the gums to help reduce inflammation and fight bacteria. Mix a drop of tea tree oil with a carrier oil, such as coconut oil, and apply to the gums with a clean cotton swab.
- Aloe vera: Aloe vera has anti-inflammatory properties and can be applied to the gums to help reduce inflammation and promote healing. Apply a small amount of aloe vera gel to the affected area.
- Oil pulling: Oil pulling involves swishing oil, such as coconut oil or sesame oil, around the mouth for several minutes before spitting it out. This can help reduce harmful bacteria in the mouth and support overall oral health.
- Turmeric: Turmeric has anti-inflammatory properties and can be mixed with water to create a paste that can be applied to the gums.
While these remedies may provide some relief, it’s important to seek professional treatment for gum infections to prevent the condition from worsening.
Gum Infection Complications

If left untreated, gum infections can lead to several complications, including:
- Tooth loss: The infection can damage the bone and connective tissue that support the teeth, which can lead to tooth loss.
- Receding gums: The gums can recede, exposing more of the tooth’s root and making it more susceptible to decay and infection.
- Abscesses: Pockets of pus can form around the teeth and gums, which can cause pain and swelling.
- Systemic health problems: Gum infections have been linked to several systemic health problems, including heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.
- Difficulty eating and speaking: Severe gum infections can make it difficult to eat or speak comfortably.
- Altered appearance: Advanced gum disease can cause the gums to pull away from the teeth, making them look longer than normal. This can affect the appearance of the smile and face.
Prevention
Prevention is key when it comes to gum infections. Here are some tips to help prevent gum infections:
- Brush and floss regularly: Brush at least twice a day and floss at least once a day to remove plaque and food particles from teeth and gums.
- Use an antiseptic mouthwash: Rinsing with an antiseptic mouthwash can help kill bacteria and reduce the risk of gum infections. The antiseptic mouthwash requires a prescription and is limited to use for a period of up to one week only.
- Maintain a healthy diet: Eat a balanced diet that is rich in nutrients and low in sugar to support oral and overall health.
- Avoid smoking: Smoking can increase the risk of gum infections and make it harder for the body to fight infections.
- Manage stress: Stress can weaken the immune system and increase the risk of gum infections. Practice stress-reduction techniques, such as meditation or yoga, to help manage stress.
- Visit the dentist regularly: Regular dental checkups and cleanings can help identify and treat gum disease at an early stage.
- Address risk factors: Address any underlying risk factors, such as diabetes or medications that cause dry mouth, to reduce the risk of gum infections.
By following these tips, you can help maintain good oral hygiene and prevent gum infections from developing.
How long does it take to treat gum infections?
The length of time it takes to treat gum infections can vary depending on the severity of the condition and how well the patient responds to treatment.
In general, it can take several weeks to several months to completely treat gingivitis. The first step in treatment is usually a thorough dental cleaning to remove the plaque and tartar buildup that is causing the inflammation. After that, the patient will need to maintain a good oral hygiene routine, including brushing and flossing regularly.
If the gingivitis is more severe, the dentist may recommend additional treatments such as scaling and root planing or antibiotic therapy. In these cases, the treatment time may be longer.
It’s important to note that even after the gingivitis has been treated, it’s essential to continue with good oral hygiene habits to prevent it from recurring. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are also important for maintaining healthy gums and teeth.
What does pregnancy have to do with gingivitis?
Pregnancy can increase the risk of developing gingivitis, which is a mild form of gum disease. During pregnancy, hormonal changes can cause the gums to become more sensitive to plaque and bacteria, leading to inflammation and swelling.
Specifically, the hormone progesterone levels increase during pregnancy, which can affect the body’s response to bacteria and increase blood flow to the gums, making them more susceptible to gingivitis. Additionally, pregnancy can also cause some women to experience changes in their eating habits and oral hygiene practices, which can contribute to the development of gingivitis.
Therefore, it is important for pregnant women to maintain good oral hygiene habits, including brushing and flossing regularly and visiting the dentist for regular checkups and cleanings.
Summary
Gum infections, also known as periodontal disease, can have serious consequences if left untreated. They can lead to tooth loss, abscesses, and even systemic health problems. However, by practicing good oral hygiene, maintaining a healthy diet, and addressing any risk factors, gum infections can often be prevented. If you are experiencing symptoms of gum disease, such as bleeding gums or bad breath, it is important to seek prompt treatment to prevent further damage. Our dental clinic in Jerusalem offers comprehensive dental services, including periodontal treatments, to help you maintain optimal oral health. Schedule a consultation appointment with us today to receive personalized care and guidance for your dental health.