Dental erosion, often overlooked in daily oral care, is a growing concern in today’s society. With an increase in the consumption of acidic foods and beverages, it’s essential to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatments of dental erosion.
What is Dental Erosion?
Dental erosion refers to the loss of the outermost layer of the tooth, called the enamel, due to acidic attack. Unlike tooth decay, which is caused by bacteria producing acids, dental erosion results directly from external acids coming into contact with the teeth.
Causes of Dental Erosion
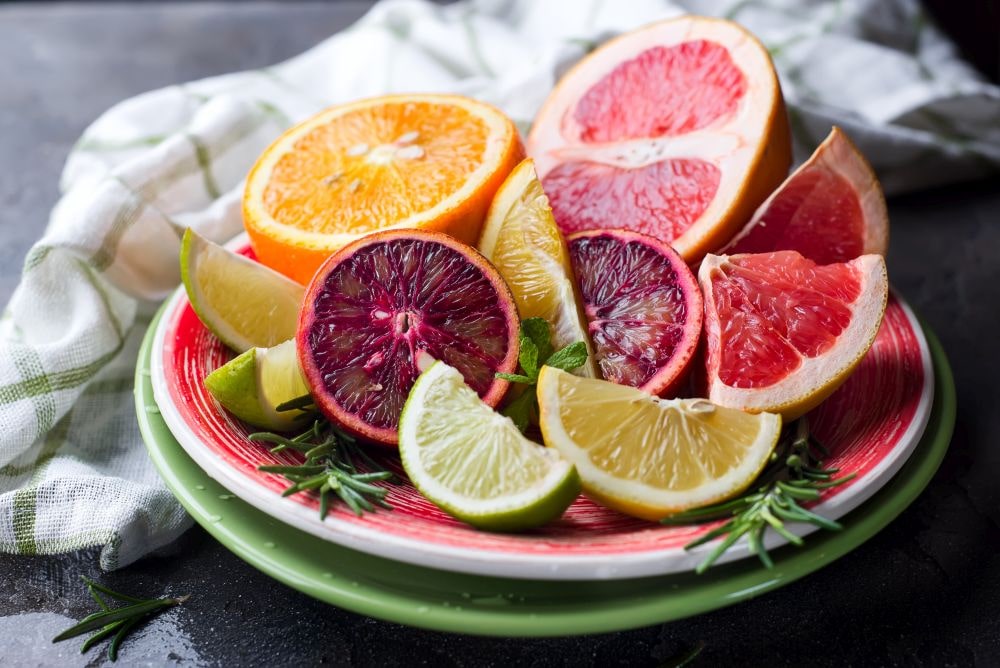
- Dietary Causes: The frequent consumption of acidic foods and drinks like citrus fruits, wine, and soda can lead to dental erosion. These substances lower the pH level in the mouth, making the environment more acidic and conducive to enamel wear.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can cause stomach acids to enter the mouth, leading to dental erosion. Frequent vomiting due to conditions like bulimia also exposes teeth to stomach acids.
- Medications: Some medicines, particularly aspirin and antihistamines, can increase the risk of dental erosion.
- Environmental Causes: Chewing on hard objects or brushing teeth too hard can contribute to wear and tear, exacerbating the effects of acid erosion.

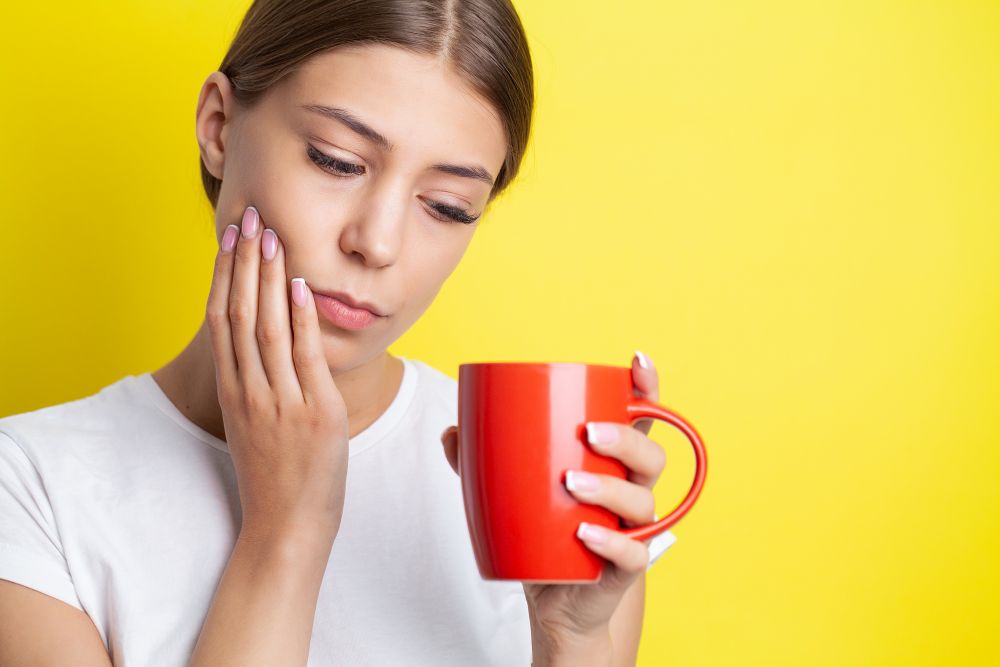
Recognizing the Symptoms of Dental Erosion
- Tooth Sensitivity: One of the earliest signs of dental erosion is increased sensitivity. You might feel a sharp pain when consuming hot, cold, sweet, or acidic foods and drinks.
- Discoloration: As the enamel wears away, the yellowish dentin beneath becomes more visible, leading to discolored teeth.
- Transparency: The tips of the front teeth might appear slightly translucent.
- Cracks and Chips: Eroded teeth can easily crack or chip.
- Cupping: Indentations can appear on the chewing surfaces of the teeth.

Treatment Options
1. Fluoride Treatment: Fluoride can strengthen the enamel, making it more resistant to erosion. Regular use of fluoride toothpaste and mouthwashes can help. In severe cases, your dentist may recommend professional fluoride treatments.
2. Dental Bonding: For teeth that have suffered significant erosion, dental bonding, where a tooth-colored resin is applied to the tooth surface, can be an effective treatment.
3. Veneers: These are thin shells made of porcelain or composite material, which can be placed over the front part of the teeth to restore appearance and function.
4. Crowns: For extensively eroded teeth, crowns can be used to restore their shape, appearance, and function.
5. Dietary and Lifestyle Changes: Reducing the intake of acidic foods and beverages, drinking acidic drinks with a straw, and avoiding brushing immediately after consuming acidic foods can help prevent further erosion.
Prevention is Key
While treatments are available for dental erosion, prevention is always the best approach. Maintaining a balanced diet, drinking plenty of water, and adhering to a stringent oral hygiene routine can significantly reduce the risk of dental erosion. Regular dental check-ups are also crucial to detect early signs of erosion and take preventive measures.
In conclusion, understanding dental erosion is pivotal for preserving our oral health. Recognizing its causes and symptoms can lead to timely intervention, ensuring our smiles remain bright and healthy for years to come.